Search technical reports
Methods for preparing durable eucalypt timber for graveyard and cellar trial
By Dean Satchell, April 2016.
Specialty Timbers NZ report 005
Executive summary
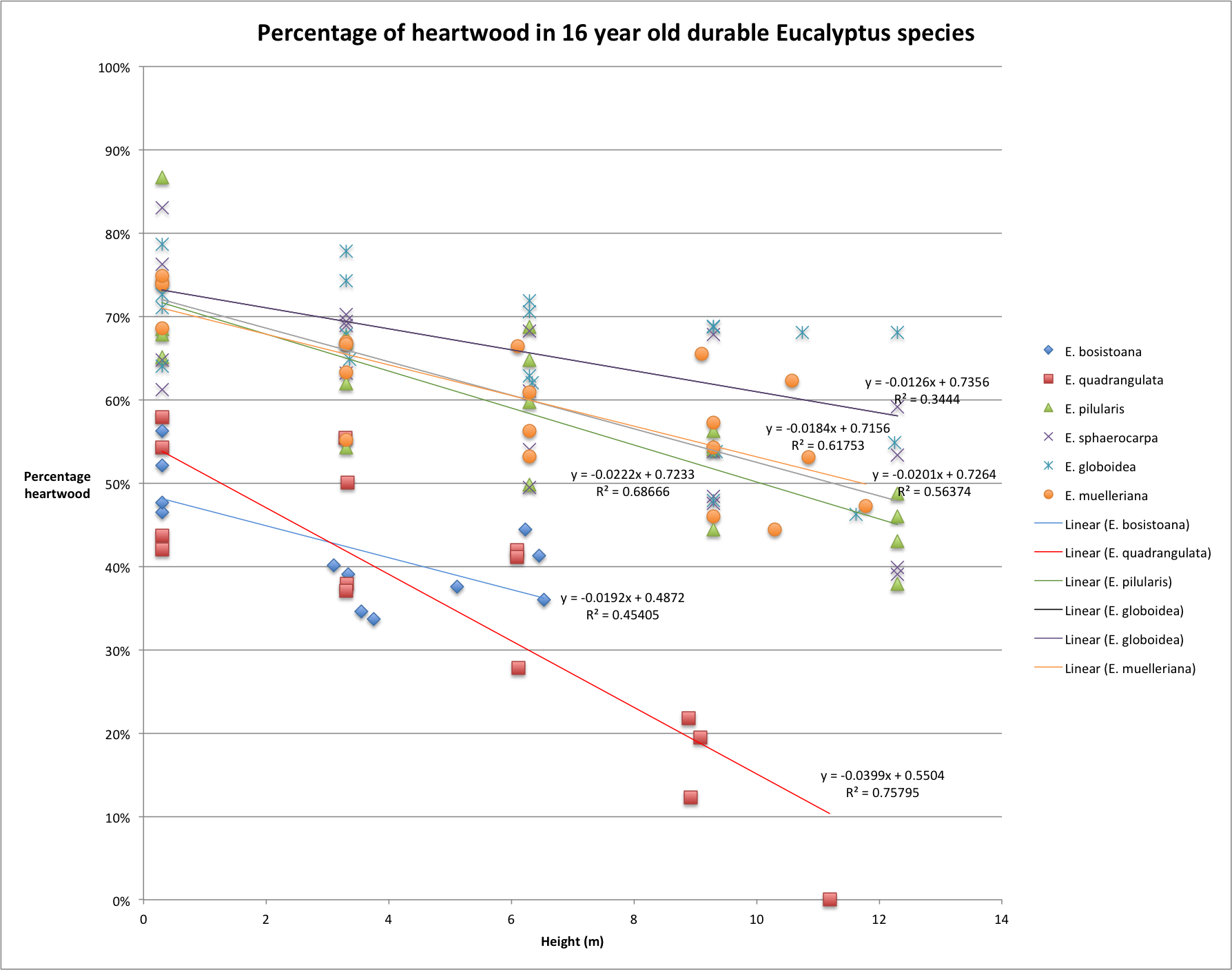
This report describes the methods used to prepare heartwood samples from six durable eucalypt species for durability testing research to be undertaken in the Specialty Wood Products Partnership programme: The decay resistance of six Eucalyptus species in stake and stakelet trials. The species were E. bosistoana, E. quadrangulata, E. pilularis, E. sphaerocarpa, E. globoidea and E. muelleriana. Trees were all 16 years old and grown in Northland.
Samples for graveyard and cellar (accelerated decay) testing from 3 m buttlogs:

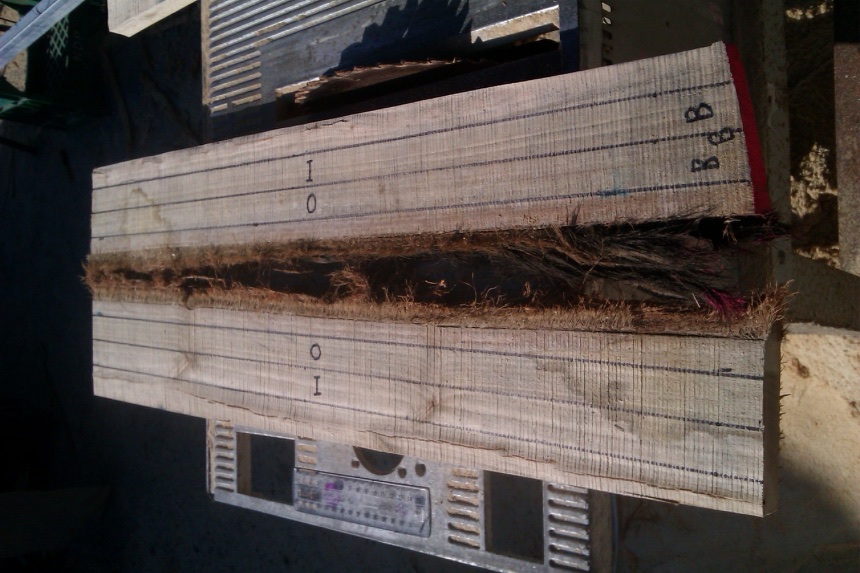
O= Outer heartwood, I= inner heartwood.
This log was smaller diameter and thus "I" was adjacent to "O"

Tree 10, log 1
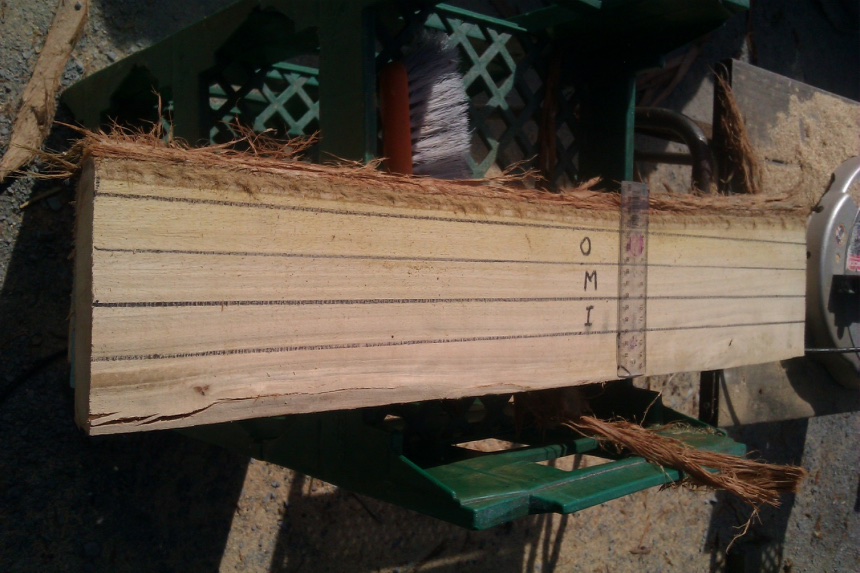
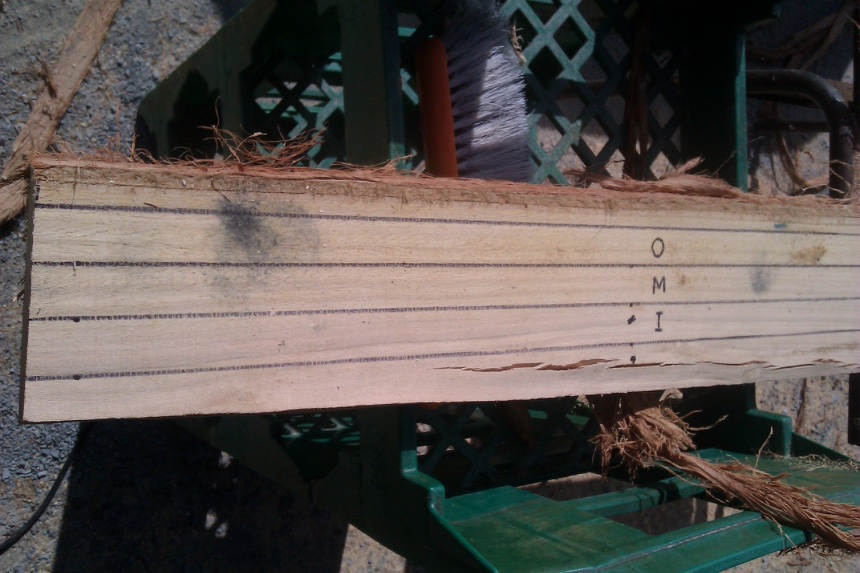
O = Outer heartwood
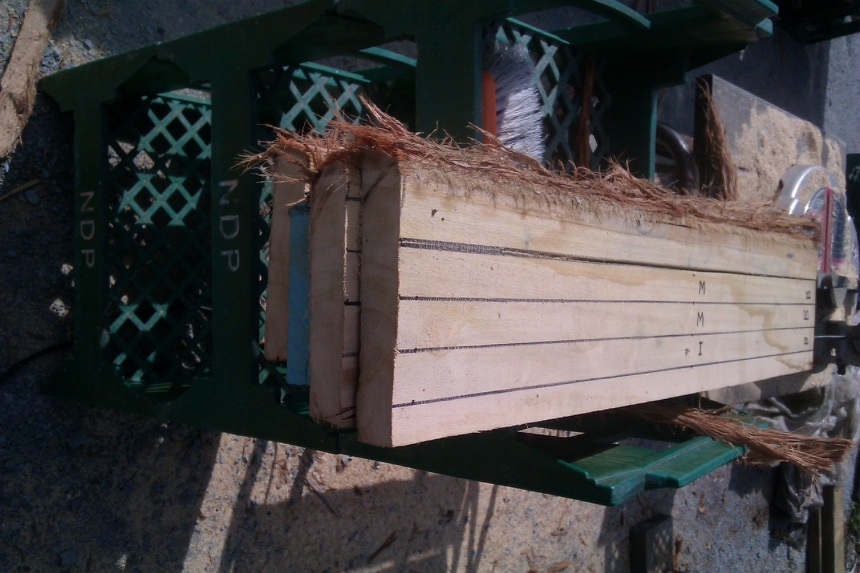
M=Middle heartwood (between outer and inner)
I = Inner heartwood, immediately adjacent to the pith.
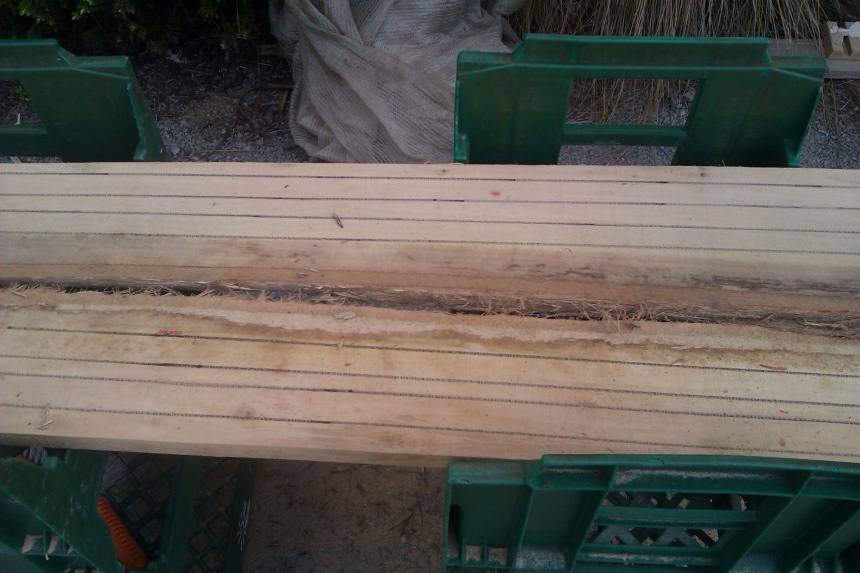

In wider diameter logs the inner heartwood stake is not immediately adjacent to the outer heartwood stake.

In wider diameter logs the inner heartwood stake is not immediately adjacent to the outer heartwood stake.
Note the red marks, one representing the inerface between sapwood and heartwood, the other suggesting that there may be intermediate wood (which is a lighter colour than the inner heartwood).

In wider diameter logs the inner heartwood stake is not immediately adjacent to the outer heartwood stake.
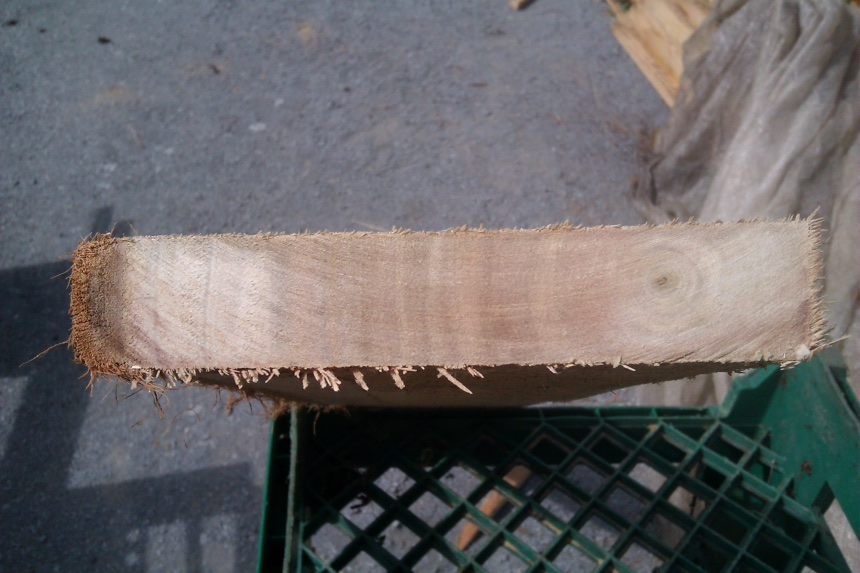

Pith and sapwood are easily seen here.

Tree 1, Log 1, this sample is both inner and outer heartwood because the diameter is too small to differentiate (usually where there is a wide sap band).
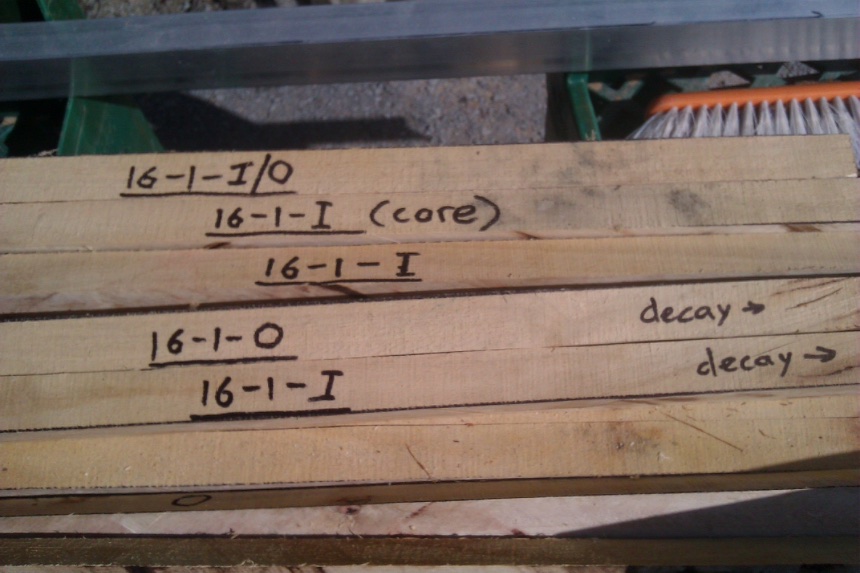
"Decay" noted on stake.
If the pith is in the stake, it was noted as (core)
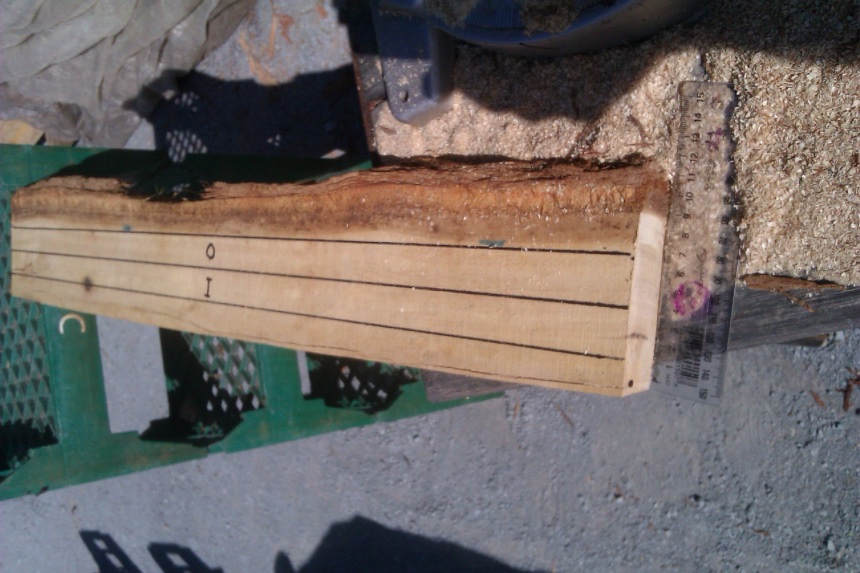

The pith was marked here with a black spot. Note the inner stake is immediately adjacent to the pith, and is closer than 3cm from the pith.
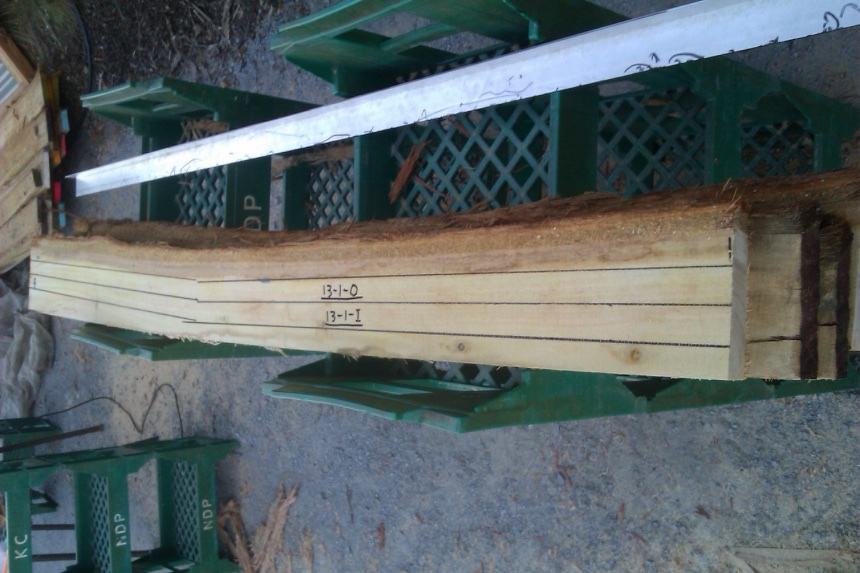

Often 3m logs were cross cut into four even sized pieces, especially where the movement was high. This allowed cutting straight 75cm stakes, which could later be cut into one 50cm graveyard stake and one 20cm cellar piece.
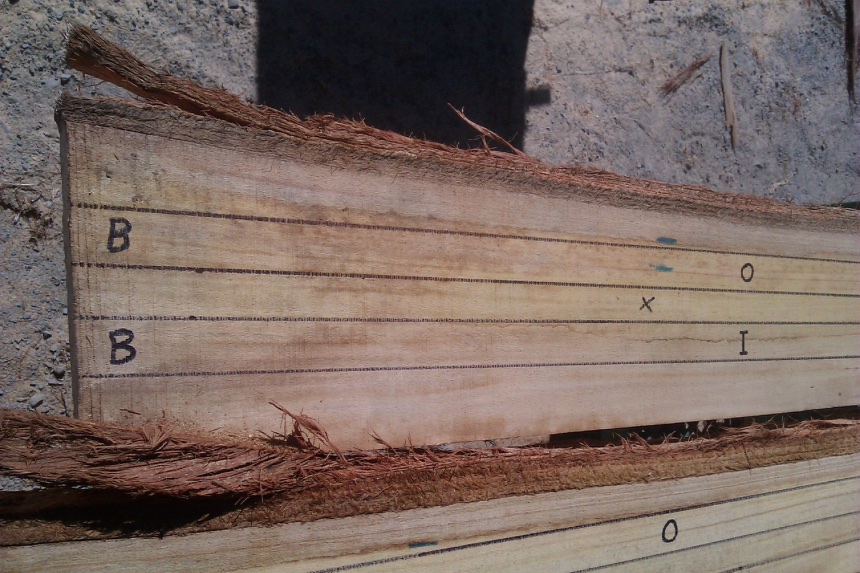

Where the butt end of the buttlog was in a stake this was marked with "B".
"x" was removed and disposed of.
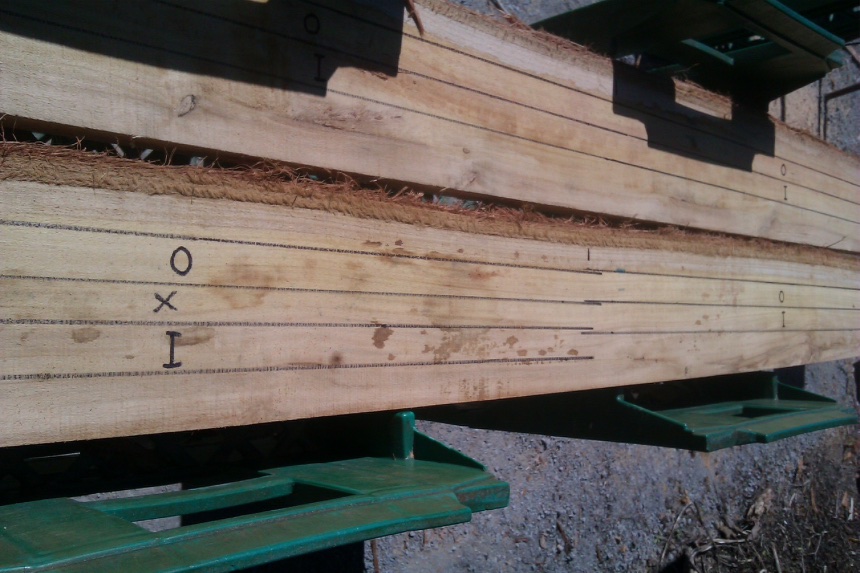
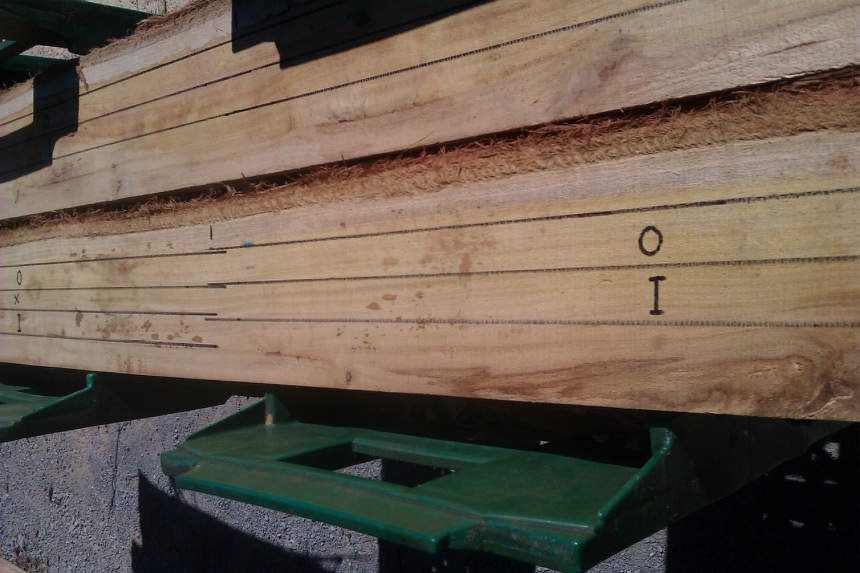
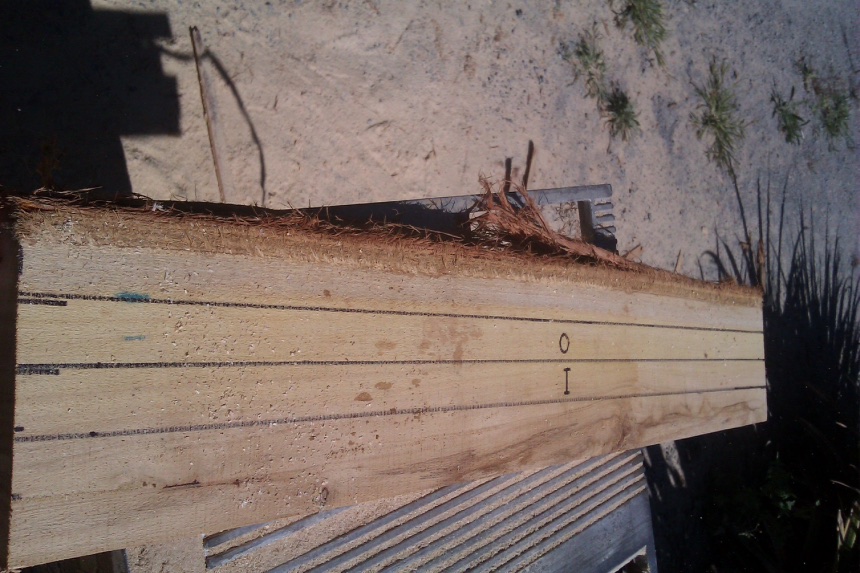



Incipient decay in the heart was avoided in cutting stakes. The "I" stake here is over 3cm from the pith.
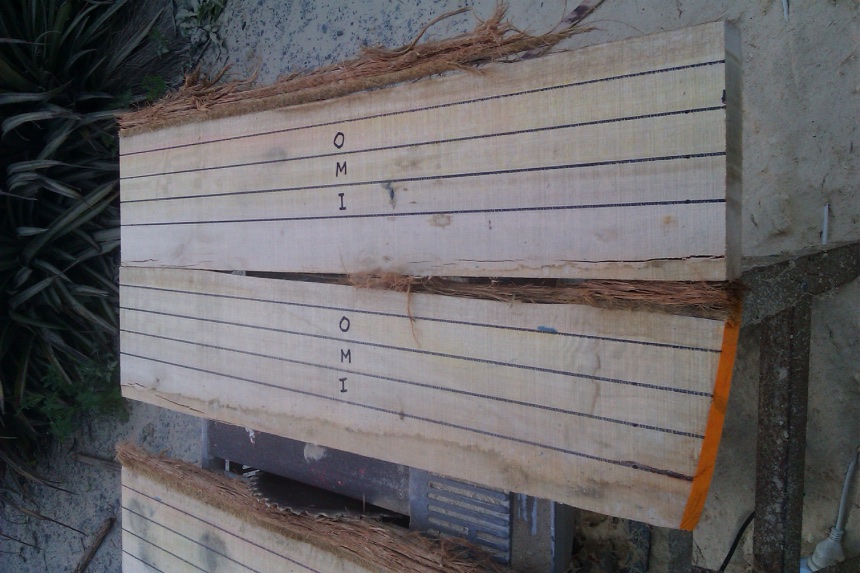
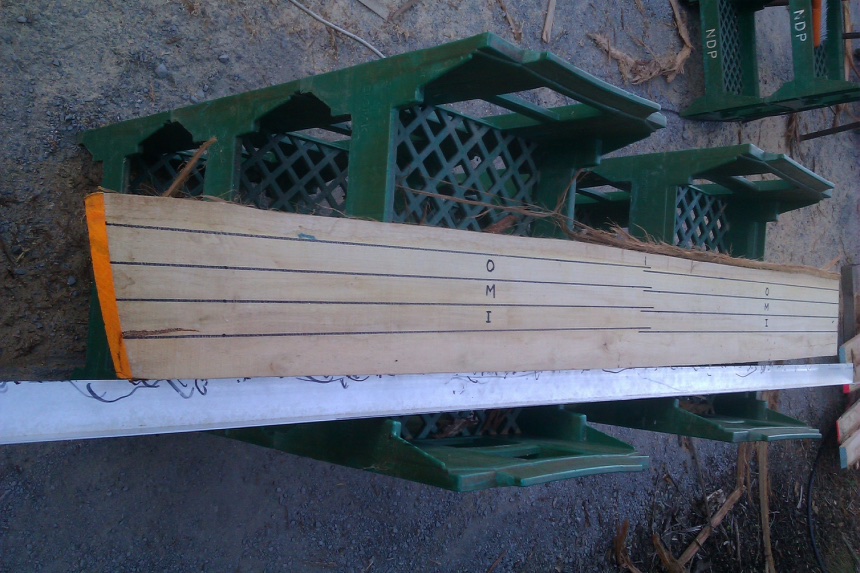







In almost every case (except where marked with (core) the pith was excluded from stakes. "I" stakes, however, were not always more than 3cm from the pith. This was not possible because of the diameters of this 16 year old thinnings material.
2018 assessment of durable Eucalypt stakes and stakelets »

 Specialty Timbers New Zealand
Specialty Timbers New Zealand
No posts yet
Add a post